
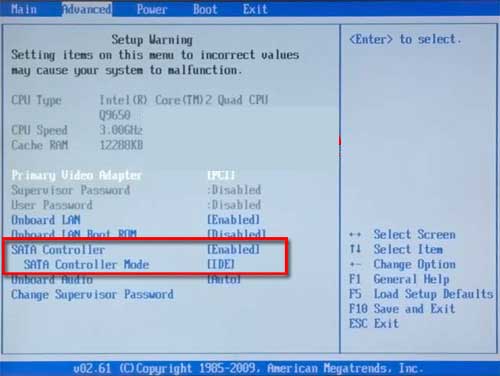
Intel recommends choosing RAID mode on their motherboards (which also enables AHCI) rather than AHCI/SATA mode for maximum flexibility. Many SATA controllers offer selectable modes of operation: legacy Parallel ATA emulation (more commonly called IDE Mode), standard AHCI mode (also known as Native Mode), or vendor-specific RAID (which generally enables AHCI in order to take advantage of its capabilities). The current version of the specification is 1.3.1. For modern solid state drives, the interface has been superseded by NVMe. AHCI is separate from the SATA 3 Gbit/s standard, although it exposes SATA's advanced capabilities (such as hot swapping and native command queuing) such that host systems can utilize them. AHCI gives software developers and hardware designers a standard method for detecting, configuring, and programming SATA/AHCI adapters. The specification describes a system memory structure for computer hardware vendors to exchange data between host system memory and attached storage devices. The Advanced Host Controller Interface ( AHCI) is a technical standard defined by Intel that specifies the register-level interface of Serial ATA (SATA) host controllers in a non-implementation-specific manner in its motherboard chipsets. content /www /us /en /io /serial-ata /ahci. Not to be confused with Arts and Humanities Citation Index.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
